Theme: Innovations in Diabetes and Endocrinology
Diabetes Conference 2024
Join the global community at the 5th Global summit on Diabetes and Endocrinology in Dubai, UAE on January 11-12, 2024. Our focus is on the theme of 'Innovations in Diabetes and Endocrinology,' welcoming participants and presenters from around the world.
The 2024 Global Summit on Diabetes & Endocrinology aims to facilitate the exchange of knowledge and expertise, offering exceptional networking opportunities for medical and industry professionals. Esteemed scientists, physicians, surgeons, young researchers, industry representatives, and students in the diabetic medicine field will convene under one roof, fostering networking and global collaboration to advance future research. This conference serves as an international platform to showcase diabetes management research, foster idea exchange, and contribute to spreading disease management knowledge for societal benefit.
Why to attend?
The Diabetes Conference 2024 focuses on the theme 'Innovations in Diabetes and Endocrinology.' This theme highlights the latest breakthroughs in preventing and treating metabolic diseases arising from diabetic and endocrine complications. The event offers in-depth discussions about approaches to diagnosis, prevention, and management of metabolic disorders. It also aims to foster the exploration of fresh concepts for treating endocrine complications.
Who Should Attend?
- Endocrinologists
- Diabetologists
- Researchers
- Practitioners and Doctors
- Students
- Nurse Educators
- Podiatrists
- Dietitians
- Eye Specialists
- Nephrologists
- Physical Trainers and Exercise Physiologists
Track 1: Diabetes: Classification and Its Associated Complications
Type 1 Diabetes: This type is primarily a result of an autoimmune response where the body's immune system targets the cells responsible for producing insulin. Although the exact cause remains incompletely understood, individuals with type 1 diabetes produce minimal insulin. To regulate their blood glucose levels, people with this type of diabetes must administer daily insulin injections.
Type 2 Diabetes: Often referred to as adult-onset or non-insulin dependent diabetes, type 2 diabetes constitutes over 90% of all cases. It is characterized by a combination of insulin resistance and inadequate insulin production, which might already be occurring when the condition is diagnosed. Initially, individuals with type 2 diabetes can manage their health through dietary adjustments and regular physical activity.
Track 2: Disorders of the Endocrine System and Diabetes
Endocrine disorders emerge when a gland generates an excessive or inadequate amount of an endocrine hormone, causing a hormonal imbalance. These disorders can arise due to the development of lesions within the endocrine system, potentially impacting hormone levels to varying degrees.
-
Adrenal Insufficiency: This condition occurs when the adrenal gland releases insufficient cortisol and sometimes aldosterone. Common symptoms encompass gastrointestinal distress, dehydration, and fatigue.
-
Cushing's Disease: Resulting from an overproduction of hormones by the pituitary gland, this disorder leads to heightened adrenal gland activity. A comparable condition known as Cushing's Syndrome can manifest, particularly in children receiving high corticosteroid doses.
-
Hypothyroidism: Arising from inadequate thyroid hormone production, this condition triggers symptoms such as fatigue, depression, constipation, and dry skin.
-
Hypopituitarism: In this scenario, the pituitary gland releases diminished or no hormones. Various underlying diseases can induce this condition, with women potentially experiencing irregular menstrual cycles.
-
Acromegaly and Growth Hormone Issues: Excessive growth hormone release from the pituitary gland can cause abnormal skeletal and bodily growth in children. Conversely, insufficient growth hormone levels can impede normal childhood growth.
-
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasias: These rare genetic disorders are hereditary and involve the development of tumors in the adrenal, parathyroid, and thyroid glands. These tumors lead to excessive hormone production.
-
Precocious Puberty: This condition involves abnormally early onset puberty, stemming from premature release of sex hormones by the glands.
Track 3: Pathophysiological Mechanisms in Endocrinology and Diabetes
Endocrine disorders are categorized based on where they originate and the level of hormone activity. High hormone activity is called hyper function, causing excessive hormone release. Low hormone activity is called hypo function, leading to reduced hormone levels.
Endocrine issues arise when a gland produces too much or too little of a hormone, creating an imbalance. Type 1 diabetes can result in a serious condition called diabetic ketoacidosis, where the body relies on fats for energy due to lack of insulin. This leads to acid build-up and is a medical emergency.
Track 4: Pediatric Endocrinology
Pediatric endocrinology focuses on kids' hormone-related issues like growth, diabetes, and puberty changes. The main condition they treat is type 1 diabetes, often making up about half of their cases.
These specialists also care for children with hormone disorders affecting growth, puberty, and glands like the adrenal, pituitary, and thyroid.
Track 5: Diagnostic Tests for Diabetes and Endocrine Disorders
-
Adrenal gland tests: Adrenal vein sampling for aldosterone and androgen levels, angiography, arterial stimulation with venous sampling, arginine stimulation test, autonomic function tests
-
Other tests: Basal acid output (BAO), simultaneous bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling (IPSS) with FRC, bone marrow aspiration
-
Hormone tests: C-peptide suppression test, captopril test, clomiphene test, calcium infusion test for medullary thyroid cancer, clonidine suppression test, daily cortisol curve, CRH test, combined pituitary function tests (CPT)
-
Diabetes tests: Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test, stress test, finger size assessment, gastric acid secretion, glucagon test, glucose tolerance test, fasting test, fine needle aspiration of a thyroid nodule (FNA), GnRH/LHRH gonadotropin-releasing hormone test
-
Further investigations: High-dose dexamethasone suppression test, hydrocortisone (HCDC), hydroxycorticosterone (18-OHB) day curve, investigations for hyperparathyroidism, cortisol (18-OHF) tests, hyperaldosteronism investigation.
Track 6: Endocrinology: Reproductive Health in Men and Women
Reproductive endocrinology is a specialized field within gynecology and obstetrics. Reproductive endocrinologists are experts in hormonal functions connected to reproduction and are crucial in managing issues related to both fertility and other dysfunctions in men and women. They have advanced training in obstetrics and gynecology, followed by specialization in reproductive endocrinology and infertility.
Men's Reproductive Health
Men with low testosterone levels may get testosterone replacement therapy. Effects can vary:
-
Reduced sexual desire, erections, and fertility
-
Decreased muscle size, strength, increased body fat, and lower bone density
-
Sleep issues
Women's Reproductive Health
Female endocrinology focuses on the menstrual cycle driven by hormones like estrogen. An endocrinologist can address:
-
Heavy, light, or absent periods
-
Premenstrual syndrome
-
Issues like ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids related to menstruation
-
Early or delayed menstruation
-
Menstrual irregularities
Track 7: Advanced Diabetes Treatment and Prevention
Assess Risk: Take a risk assessment to gauge your chance of developing type 2 diabetes. A score of 12+ indicates high risk and eligibility for the LIFE program—an initiative aiding in risk reduction.
Maintain Weight: Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, increases insulin resistance and diabetes risk.
Stay Active: Regular moderate exercise helps manage weight, lower blood sugar, and improve blood pressure and cholesterol.
Eat Well: Opt for a balanced diet with fewer fats, more fruits, vegetables, and high-fiber foods. Cut down on salt.
Avoid Processed Foods: Ready-made meals tend to be high in salt, fats, and calories. Cooking fresh ingredients is better.
Limit Alcohol: Excessive alcohol raises weight, blood pressure, and triglycerides. Men: 2 standard drinks/day, Women: 1.
Quit Smoking: Smokers are twice as likely to get diabetes.
Manage Blood Pressure: Exercise, balanced diet, healthy weight help. Medication may be needed in some cases.
Reduce Cardiovascular Risk: Diabetes and heart disease share risks like obesity and inactivity.
Track 8: Diabetic Kidney Problems
Diabetic nephropathy is kidney damage due to diabetes, which can lead to kidney failure. High sugar levels harm tiny blood vessels that filter waste from our blood. Excess salts and water are retained, causing swelling and weight gain. Kidney function declines, often unnoticed in early stages. Regular urine tests are important to detect damage.
Diabetes can also harm nerves, affecting bladder control and kidney health. Holding urine too long can cause infections due to high blood sugar.
Around 10-40% of type 2 diabetes and 30% of type 1 diabetes patients may face kidney failure.
Track 9: Diabetic Retinal Pathology
Diabetic retinopathy happens when blood vessels in the retina are damaged due to unstable blood sugar levels. This can cause swelling, fluid leakage, and unusual new blood vessels. Scar tissue might lead to retinal detachment.
Early signs include blurry vision, floaters, dark spots, and color perception issues. While not curable, diabetic retinopathy can be managed with laser treatments or surgery like vitrectomy for better vision.
Track 10: Diabetes and Skin Issues
Diabetes can impact the skin, aiding in early diabetes detection. Many skin problems are treatable. Specific issues like necrobiosis lipoidica, diabetic dermopathy, eruptive xanthomatosis, and diabetic blisters are often linked to diabetes.
Track 11: Diabetes and Heart-Related Conditions
Diabetes raises the risk of heart problems (6% of people). Atherosclerosis, which narrows arteries, can reduce heart blood flow. Blocked heart arteries cause angina or stroke. Atherosclerosis also causes strokes and poor leg blood supply. These are top causes of death in diabetes.
Track 12: Dietary Regulation and Body Weight Management
A healthy diet is vital for preventing diabetes-related issues. Active lifestyle and good eating habits are important. Focus on low-carb, like whole grains, veggies, fruits, nuts, and low-fat foods. High fiber is good. Methods include carb counting, glycemic index, My Plate, and TLC diet.
Track 13: Diabetic foot and ankle
People with diabetes must check their feet often to prevent amputation risk. Even small wounds like blisters can be serious due to slow wound healing and reduced blood flow. Common bacteria causing infection include streptococci and staphylococci. Proper treatment is crucial for chronic or treated wounds with microbial cultures.
Track 14: Biomarkers of diabetes
A biomarker is a gene, molecule, or trait that helps detect diseases like diabetes. HbA1c is a biomarker for spotting risks of retinopathy, vascular issues, and nephropathy. It aids prevention in early stages. Using biomarkers in developing diabetes drugs helps understand the disease process faster.
Track 15: Diabetes-Related Complications and Their Management
Managing diabetes and its complications aims to balance carbohydrate metabolism. For insulin deficiency, insulin pumps or injections are used, while insulin resistance is managed with exercise and diet. Treating or preventing other disease-related complications is crucial. A healthy diet is key to a healthy life.
Diabetes links to secondary conditions and heart diseases. Regular checks of blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and eye exams prevent complications like diabetic retinopathy.
Track 16: Thyroid disorders
The thyroid gland, shaped like a butterfly at the neck's base, is vital for body coordination. It makes hormones that manage metabolism. Too little hormone causes hypothyroidism, while excess leads to hyperthyroidism. Thyroid problems are common in women, affecting fertility, pregnancy, and periods.
Graves' disease is an immune disorder causing excessive thyroid hormone production, known as hyperthyroidism. Hormone metabolism is controlled by carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Track 17: Genomic Endocrinology
Genomic endocrinology involves using genetics to understand endocrine functions and disorders. Genetic mechanisms cause endocrine diseases, and studying genetic mutations provides insights into their causes.
Analysis of the Endocrinology Drugs Market
Anticipated growth in the endocrinology drugs market is projected at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period from 2022 to 2027.
Segmentation of the Endocrinology Drugs Industry
In accordance with the report's scope, endocrinology pertains to the field of physiology and medicine focusing on hormones and endocrine glands. Drugs addressing disorders of these glands fall under the category of endocrinology drugs. The Endocrinology Drugs Market is categorized by Therapy Area (Adrenal Insufficiency, Diabetes, Thyroid Hormone Disorder, and Other Therapy Areas), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies), and Geographic Regions (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, Africa, and South America). The report also provides insights into market sizes and trends across 17 different countries in key global regions.
Endocrinology Drugs Market Trends
Diabetes Expected to Lead the Market in the Forecast Period
Diabetes ranks as the most prevalent endocrine disorder in the United States. According to data from the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the number of people with diabetes increased from 34.2 million in 2018 to 37.3 million in 2020. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) reported in November 2021 that 1 in 6 adults worldwide lives with diabetes, with nearly half of those with diabetes in Mexico remaining undiagnosed. In the North America and Caribbean region, 1 in 7 adults (51 million) are affected by diabetes, according to the same source.
Moreover, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's 2021 updates indicate that new diabetes cases among U.S. adults aged 18 years and older numbered 1.4 million in 2019. Among adults aged 45 and older, the incidence of diagnosed diabetes increased significantly compared to those aged 18 to 44 years. This notable rise in new cases with age, particularly between 45 and 64 years, is expected to drive the demand for endocrinology drugs throughout the forecast period.
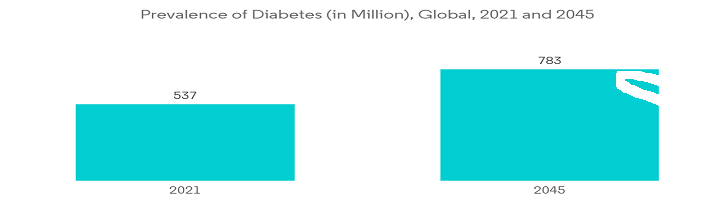
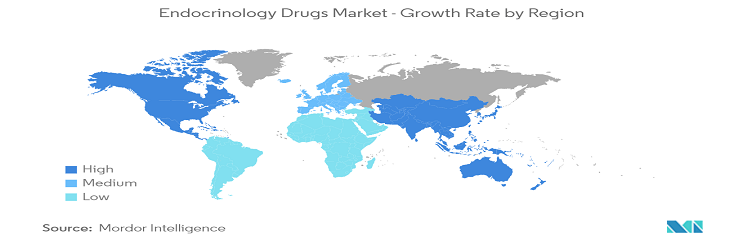
North America's Expected Market Dominance in the Forecast Period
North America is projected to hold a significant market share due to its robust healthcare infrastructure, high rates of obesity, unhealthy dietary habits, changing lifestyles, and continuous introduction of new products. For instance, in August 2021, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved the rapid-acting insulin Lyumjev (insulin lispro-aabc injection) 100 units/mL, indicated to enhance glycemic control in adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the approval of the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin product, Semglee (insulin glargine-yfgn), was granted by the United States Food and Drug Administration in July 2021.
These approvals are expected to bolster growth in the endocrinology drug market. Furthermore, Rybelsus received Health Canada's approval in April 2020 for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults. Considering these factors, North America is poised to maintain its dominance in the endocrinology drugs market throughout the forecast period.
Conference Highlights
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | January 11-12, 2024 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Diabetic Complications & Medicine
- Endocrinology & Diabetes Research
- Journal of Clinical and Molecular Endocrinology
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by





